Oral Surgery
- Introduction
- Extractions
- Wisdom teeth
- Bone grafting
- Jaw surgery
- Gum surgery
Introduction
Oral-Maxilofacial surgery is a surgical specialty which involves the diagnosis, surgery and adjunctive treatment of diseases, injuries and defects in the head, neck, face, jaws and the hard and soft tissues of the oral (mouth) and maxillofacial (jaws and face) region.
Procedures:
- Tooth extraction or tooth removal
- Wisdom tooth removal
- Bone graft and Ridge augmentation
- Sinus lift
- Jaw surgery
- Alveoloplasty
- Alveolectomy
- Vestibuloplaty
- Cystic or pathologic lesion removal
- Embedded removal
- Nerve re-positioning

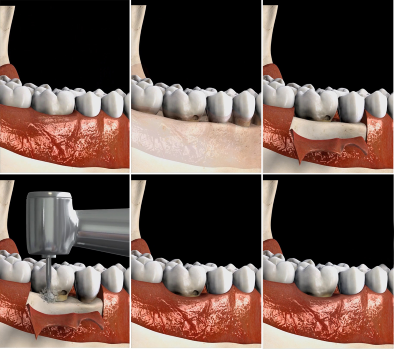
Extractions
Teeth extraction is a process to remove a tooth under the following conditions out :
Severe gum disease: severe tooth mobility/severe bone loss
- Unrestorable tooth
- Untreatable infected tooth
- Malposition or malfunction tooth
- Orthodontic treatment purpose
Chair time taking for each tooth extraction is different depending difficulty.
If the tooth left very less due to the severe decay of breaking, treatment may take longer time than usual case.
X-ray examination is necessary prior to tooth extraction.
Wisdom teeth
Occasionally an impacted tooth or wisdom tooth ( Third molar ) requires tooth extraction because it can’t erupt normally. or or they are not aligned properly. For most people, the eruption process takes place during their late teens or early twenties Main cause is lacking of space in the mouth or evidence of pathological sign present on the tooth.
Risks of keeping impacted or wisdom tooth.
- Pericoronitis / Infection
- Complications associated with tooth decay
- Periodontal disease (gum disease)
- Pathology – Cysts, tumors. ( Rare )
- Risk of damage to adjacent teeth / Root resorption
- Chronic pain or discomfort
- Problems associated with poor tooth alignment
Types
- Fully erupted wisdom tooth
- Partial erupted wisdom tooth
- Complete bony impacted tooth
Each type requires different treatment duration and fee. Degree of pain and swelling will be different on each patient depending on type of wisdom tooth, difficulty of procedure and aindividual response.
Bone grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair a bony defect. There are several procedures as the following:
- Guided bone regeneration (GBR) is a surgical procedure that utilizes grafting materials and barrier membranes to stimulate and direct the growth of new bone into defect sites.
Autogenous bone and/or a biomaterial, is placed into the bony defect to maintain space and stimulate formation of new bone. The filled defect is then covered with a barrier membrane to assist in wound-healing and prevent the ingrowth of soft tissue.
GBR approaches are used to restore bone in cases of fenestration or dehiscence defects around an implant, to compensate for major bone deficiencies, or to avoid bone resorption after tooth extraction in deficient alveoli.
- Tooth loss, trauma or tumor resection can lead to large bony defects in the alveolar ridge. In these situations, reconstructive measures are indicated to augment the quantity of bone.
Autogenous bone block grafts harvested from the lower jaw or the iliac crest are the principal material used to reconstruct larger alveolar ridge defects.
- A sinus lift sinus augmentation s surgery that adds bone to the area of upper molars and premolars. To make room for the bone, the sinus membrane has to be moved upward, or “lifted.” This procedures can be conducted before implant placement (twostage surgery) or simultaneously (single surgery). The posterior maxilla residual bone and sinus anatomy must be analyzed prior to planning the procedure and determining the timing of implant placement.
- For Periodontal treatment : The use of biomaterials for guided tissue regeneration (GTR) is more effective than open flap debridement alone in resolving periodontal defects. During this procedure the defect is filled with the bone substitute Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen® and covered with the collagen membrane Geistlich Bio-Gide® Perio.
Bone substitute materials should:
- Fill the osseous defect and reduce pocket depth
- Generate increased levels of clinical attachment
- Stimulate regeneration and preservation of the patient’s own bone and periodontal
Collagen barrier membranes should:
- Stabilize the bone graft
- Exclude epithelial down-growth
- Allow alveolar bone cells to repopulate within the defect
Treatment fee for Bone grafing depends on the method and amount of sythetic bone material.
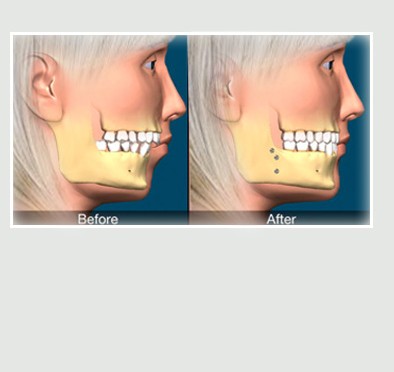
Jaw surgery
Jaw surgery or Orthognathic surgery is a type of following surgery
– combining with orthodontic treatment in order to correct jaw position and malocclusion.
– congenital conditions like cleft palate
The procedure has to be done under general anesthesia by oral and maxillo facial surgeon. Treatment can involve single or double jaws depending on the indication and treatment plan. Plate and screw to attach each particular bony part will be necessary.
When the jaws are moved forward or backward, up or down, or rotated, the facial soft tissue in the chin, cheeks, lips and tip of the nose moves accordingly. Therefore, once the jaws are correctly positioned in harmony with facial features. This results to a better facial profile.
The main purpose of orthognathic surgery is to improve your bite function but with a result of better facial profile, many patients can improve their character, personality, and speaking, leading to a better quality of life.
Orthognathic surgery can also be referred to as corrective jaw surgery.
Gum surgery
There are various kinds of gum surgery to improve or enhance other dental procedures such as a crown or filling.
Some common gum surgery procedures:
1) Crown lengthening
For patients who have periodontal disease causing pockets to form, or who have had a tooth break at or below the gum line, functional crown lengthening can allow access to more of the tooth’s surface for remedial dental work or gum treatment.
The crown lengthening procedure is also known as gum contouring. Excess gum tissue is carefully removed to expose more of the tooth surface and reduce gingival pockets that harbor bacteria. If the tooth is broken, the gum line can be lowered to allow access for the placing of a restoration.
Occasionally, esthetic crown lengthening may be performed to reduce the look of a “gummy” smile and provide a more even, attractive looking gum line.
Procedure
The procedure takes between one and two hours and can be performed on a single tooth or on several teeth to reduce the depth of periodontal pockets.
Gum contouring is performed under local anesthetic and may involve removing a small amount of bone tissue or reshaping the end of a broken tooth while removing overlapping gum tissue, allowing for a restoration to be placed.
Small sutures will be placed and the gums allowed healing. If a restoration is being placed, it may be done in the same visit.
Benefits
- can improve gum health by reducing pockets between the gum and the tooth and
- reducing chances of infection.
- Functional crown lengthening can also provide a more stable foundation for a needed restoration.
- Functional gum contouring promotes healthier gum condition and proper tooth restoration.
This procedure is to remove a triangle-shaped slice of tissue on distal side of lower last molar teeth. It may be used to remove a tumor or some other type of tissue that requires removal and typically includes a small amount of normal tissue around it. It is easy to repair, does not greatly distort the shape of the underlying organ and leaves just a single stitch line as a residual.
This surgery is performed to increase access for scaling and root planning in order to remove plaque and calculus below the gum line. The pockets and position of the gums are reduced to minimize areas where disease-causing bacteria can hide. During this procedure, the gum tissue is folded away from the tooth and disease-causing bacteria removed from the root surface through scaling and root planing with hand and ultrasonic instruments, before securing the tissue into place with stitches.