General Dental Care
- Digital X-ray Exam
- Cleaning
- Bonding
- Gum treatment
- Root Canal Therapy
- Bad Breath
Digital X-ray Exam
Dental x-ray are the one of the diagnostic tool to see internal dental structure and surrounding structure like Dental caries, infection and bone condition etc.
It’s possible for tooth decay, apical root infection, defective restoration, periodontal disease, etc. to be missed during a clinical exam, and radiographic evaluation of the dental and periodontal tissues is a critical segment of the comprehensive oral examination.
Benefits of a Digital X-ray System:
- The images are displayed instantly.
- An enhanced, larger, clearer picture than conventional x-ray resulting in better diagnostic outcome.
- Can be recorded as a digital file which is easy and convenient for tracking.
- Better for the environment because there is no use of toxic processing chemicals or lead foil that are in the conventional dental film system.
- Produces a fraction of the radiation required for the conventional x-ray system.
Type of dental x-ray:
1) Extraoral x-ray:
1.1) OPG
An OPG is a panoramic or wide view x-ray of the lower face. All the teeth of the upper and lower jaw are presented on a single film.
Benefit:
- A general overview of the teeth and the bone which supports the teeth.
- It demonstrates the number, position, and growth of all the teeth including those that have not yet surfaced or erupted.
- Jawbone problem detection.
- Temporomandibular joint, or TMJ, evaluation.
- Orthodontic treatment planning.
- Wisdom teeth assessment.
- Maxillary sinus evaluation.
- Mandibular nerve evaluation.
1.2) Lateral Cephalometric x-ray:
A Ceph or Lat Ceph is a lateral or side view x-ray of the face, which demonstrates the bones and facial contours in profile on a single film. This type of x-ray is commonly used in orthodontic treatment diagnosis and planning.
2) Intraoral x-ray:
2.1) Bitewing x-ray
Benefit:
- Interproximal caries
- Recurrent caries under existing restorations.
- Bone support determination in extensive bone loss case
2.2) Periapical x-ray:
Benefit:
- Show the whole tooth ; from the crown, to the root area where the tooth attaches into the jaw.
- Each film shows all teeth in one portion of either the upper or lower jaw.
- Use to detect any unusual changes in the root and surrounding bone structures.
Cleaning
Patients should see dentists for cleaning or scaling and polishing every 6 to 12 months depending on the case.
In dental cleaning, dental hygienist remove deposits such as plaque and calculus ( tartar ) from tooth surfaces. Over time, the regular removal of these deposits may reduce gingivitis (a mild form of gum disease) and prevent progression to periodontitis (severe gum disease).
Upon cleaning, dentists can evaluate overall teeth condition and check for other possible problems such as dental caries, gum disease, infection and etc.
Such problems can be detected by visual examination and x-ray.
Scaling and polishing will be done by dental scaler machine, dental hand instruments and dental prophylaxis.
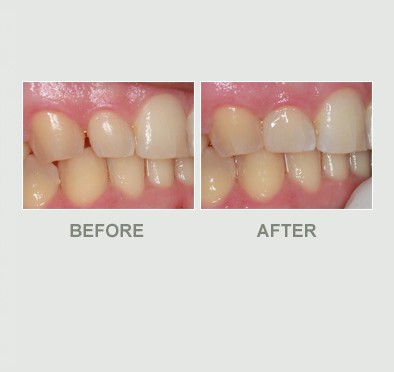
Bonding
A dental filling is a method to replace damaged tooth structure such as dental caries ( decay or cavities ) case or broken parts.
In addition, we can also use dental fillings for cosmetic treatments such as gap closure, tooth shape transformation such as facing or veneer and etc.
There are 2 kinds of dental fillings
1. Dental composite filling
Nowadays, we use composite filing or tooth color filling as first treatment of choice.
There are several types and shades of composite fillings that Dentist can select to match your teeth best especially in front teeth area.
2. Amalgam filling
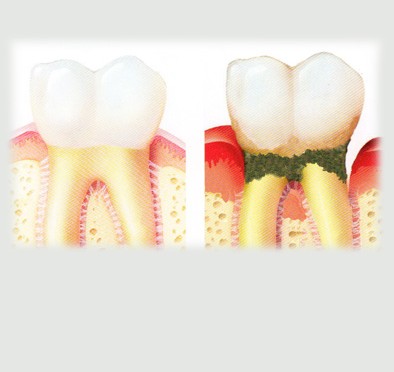
Gum treatment
Each tooth is attached to the bone by an elastic tissue, so called ‘Periodontal Ligament’.
That means our tooth roots are surrounded by the bone.
Gum or gingival tissue will cover the bone, similar to our skin covered on our body.
Once there is a damage to the gum, bone or periodontal tissue, patients will need Periodontal treatment.
Possible factors for Periodontal damage:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Genetic problems
- Effect from certain medical illness
- Traumatic force
- Poor dental filling, crown, veneer, bridge margin
- Root canal infection
- Overloading force from denture clasp
- Malocclusion
Comprehensive Periodontal Evaluation is required for proper treatment planning which includes clinical examination and full mouth x-ray examination.
Treatment methods:
- Basic treatment:
- Moderate to severe case:
Root Canal Therapy
Our teeth are not only a single layer. In fact, they consist of three layers: “Enamel” First layers) “Dentine” (second layers ) and “Dental Pulp” (Third layers).
A dental pulp contains nerve and blood vessels. When the infection occurs at the pulp or third layer of a tooth, at that time tooth need root canal treatment or Endodontic treatment. Pulp infection is caused by bacteria that live in the mouth and invade the tooth.
Causes of dental pulp damage:
- Deep dental caries
- Traumatic force
- Broken tooth from accident
- Tooth displacement from accident
- Gum disease
- Chronic infection from adjacent teeth
- Tooth wear from chronic mechanical or chemical damage
- Intentional tooth preparation for cosmetic treatment
Treatment processes:
- Access opening
- Pulp or nerve removal or existing root canal filling removal
- Root length measurement by apex locator and x-ray machines
- Mechanical instrumentation by endodontic files and rotary instrument. This is a an important step which should be done by dental microscope. This will help prevent possible complication. The endodontic files will clean and smooth out root canal wall to eliminate all the bacteria accumulation.
- Root canal medicament consideration
- Root canal filling by system B obturation system and root canal filling material If endodontic treatment or first root canal treatment was done in the past and there remains root infection, endodontic retreatment or root canal retreatment is recommended. A typical cause of remaining root canal infection is from untreated root canal. Dental microscope will help to magnify the root canal Mostly, root canal retreatment requires a step of root canal medication for at least a week prior to the root canalobturation.
Number of treatment visits and duration:
| Condition | Number of visits |
| Non apical infection tooth | Single visit |
| Intentional root canal treatment | Single visit |
| Apical infection tooth | At least 2 visits with 1 week apart |
| Root canal retreatment | At least 2 visits with 1 week apart |
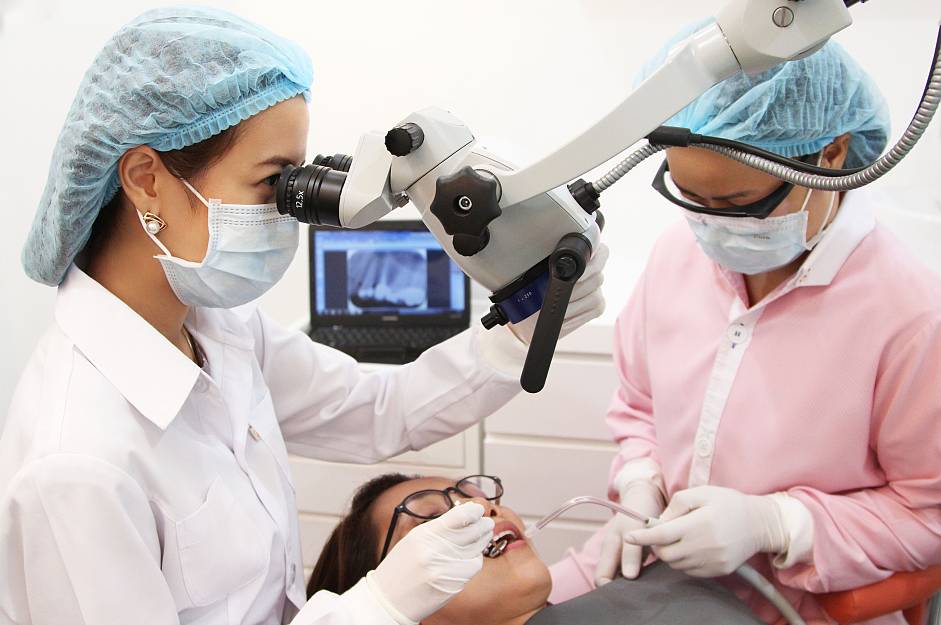
At Truth dental clinic, Root canal treatment will is performed under OPMI dental microscope by skillful root canal specialist or endodontist.
In the 21st century the OPMI plays a vital role in endodontics and endodontists have led the way in embracing the OPMI into daily clinical practice. Endodontic treatments can be very challenging due to the complexity of the anatomy of the root canal system. In the past root canal treatment was performed predominantly by feel. With the aid of the OPMI, structures can be seen that remain hidden to the naked eye and treat- ment can be carried out with far greater precision and predict- ably than ever before. Microscopy in endodontics has become a way of life
Benefit of having OPMI microscope in root canal treatment
- Examination of the external surface of the tooth
- Removal of coronal restorations
- Preservation of tooth structure
- Identification of the floor of the pulp chamber
- Location of sclerosed canals
- Identification and orientation of curvatures in the radicular access
- Identificatio of internal cracks, ledges and blockages in the root canal
- Evaluation of canal cleanliness after preparation
- Ensure optimal obturation
- Assessment of existing root fi lings
- Identificatio and management of perforations
- Assessment of coronal leakage
- Evaluation of endodontic instruments after use
- Removal of root fi ling materials in non-surgical re-treatment
- Management of soft and hard tissues in surgical re-treatment

Bad Breath
Halitosis, commonly known as bad breath, is an embarrassing health condition that affects approximately 30% of people around the world. Bad breath odors vary, depending on the source or the underlying cause.
Some of the common causes of bad breath are the following:
1) Dental factors:
1.1) Dental cavities
1.2) Gum disease
Gingivitis and periodontal disease can also cause bad breath when left untreated, and the odor will only be masked by outside agents, not cured. Identifying and treating gum disease is the only way to stop periodontal bad breath.
Keeping your mouth free from bacteria and plaque is the best line of defense against bad breath. If you have persistent bad breath that is not caused by medication, food choices, or dry mouth, ask for a periodontal consultation to check for gum disease.
1.3) Infection
1.4) Defective dental restoration or any dental appliances
Badly fitting braces, bridges, and dentures can allow food particles to become trapped and cause halitosis. Having dental appliances checked and refitted regularly can help avoid this issue.
2) Non pathological factors:
2.1) Food choices.
Many foods can cause bad breath – especially those which are strongly flavored, spicy, or which have a strong odor on their own, such as fish or cheese. Meat can cause bad breath more than vegetables. Avoiding such foods or brushing and flossing immediately after eating can help prevent them from causing bad breath. Mouth sprays, strips, and mints can also help.
2.2) Alcohol consumption
2.3) Tobacco use
Chewing and smoking tobacco products not only causes bad breath, but significantly increases the risk of gum disease.
2.4) Oral dryness
Some people have dry mouth naturally; others take medications which have dry mouth as a side effect. When saliva isn’t present to continually wash the gums and teeth, decay of bacteria present in the mouth causes bad breath. Chewing gum can help prevent dry mouth.
2.5) Hunger breath
2.6) Snoring or mouth breathing
Can cause morning breath greater than in a normal case.
3) Pathology factors:
3.1) Respiratory system
3.2) Gastrointestinal tract disorder
A flatulence or constipation condition can also cause bad breath.
3.3) Abnormal accumulation of certain substance in blood circulation.
For example: acetone odor in a diabetes patient, urine breath from a kidney problem, and amine breath from a liver problem.
Clinical and x-ray examination is necessary to find out if you have any dental factors and to provide you with a treatment solution. If there are no dental factors relating to the bad breath condition, our dentist can recommend you to getting further medical advice or a consultation.








